Unveiling TikTok Advertising Secrets
Explore the latest trends and insights in TikTok advertising.
Decoding the Mind: Why Search Intent is Your New Best Friend
Unlock the secret to skyrocketing your traffic! Discover how understanding search intent can transform your content strategy.
Understanding Search Intent: The Key to Unlocking Effective Content Strategies
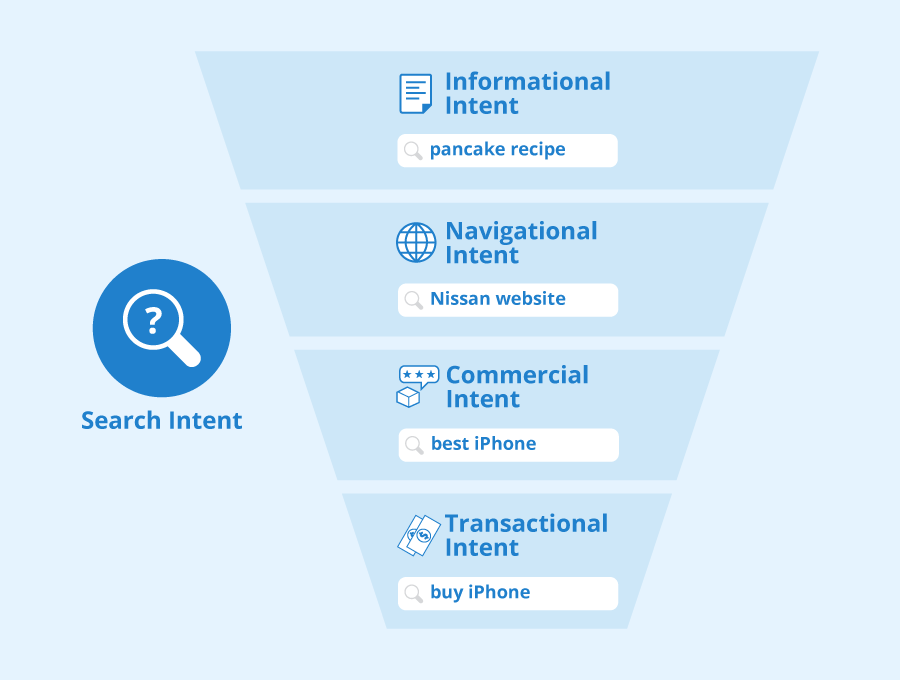
Understanding search intent is crucial for developing effective content strategies that resonate with your audience. Search intent refers to the underlying motivation behind a user's query, whether they're seeking information, making a purchase, or looking for a specific website. By identifying the four primary types of search intent—informational, navigational, transactional, and commercial investigation—content creators can tailor their content to meet the needs of their audience. For instance, if a user is searching for 'how to train a puppy,' they likely have an informational intent, and providing a comprehensive guide or informative articles can help fulfill that need.
Moreover, diving deeper into search intent allows marketers to strategically align their content with the stages of the buyer's journey. By analyzing keywords and understanding what users expect when they type those queries, brands can create targeted content that guides users closer to conversion. For example, targeting transactional search intent with phrases like 'buy running shoes online' should lead to product pages that showcase your offerings prominently while addressing user concerns, such as reviews and pricing. Ultimately, tapping into users' search intent not only enhances user satisfaction but also drives higher traffic and improved SEO performance.
The Psychology Behind Search Intent: What Your Audience Really Wants
The concept of search intent is fundamental to understanding what your audience truly desires when they input queries into search engines. It encompasses the underlying motivation or reason why a user performs a search, whether they are in pursuit of information, looking to make a purchase, or seeking a specific location. By deciphering these intents, content creators can tailor their material to better align with the needs of their users. For instance, queries categorized as informational might warrant in-depth articles or guides, while transactional searches could require compelling product descriptions or reviews that facilitate decision-making.
To effectively tap into search intent, businesses and bloggers should conduct thorough keyword research to analyze user behavior and preferences. Utilizing tools that uncover the types of content that perform well for various queries can greatly aid in this process. Additionally, understanding different types of search intent, such as navigational, informational, and transactional, allows content creators to categorize their material more effectively. By delivering content that meets these intents, brands can not only enhance user satisfaction but also improve their SEO rankings, as search engines increasingly prioritize user experience.
How to Align Your Content with User Intent for Better Engagement
Understanding user intent is crucial for creating content that resonates with your audience and drives engagement. User intent refers to the purpose behind a user's search query—whether they are looking for information, seeking to make a purchase, or trying to navigate to a specific website. To align your content with user intent, start by conducting thorough keyword research. Identify the primary keywords and phrases that represent what your audience is searching for and categorize them into three main types: informational, navigational, and transactional. This will help you tailor your content accordingly.
Once you have a clear understanding of user intent, it's essential to create content that directly addresses these needs. For example, if users are seeking information, develop comprehensive guides or how-to articles that provide valuable insights. On the other hand, transactional intent may require product descriptions or comparison articles. Engagement can be further enhanced by incorporating multimedia elements, such as images or videos, to make the content more appealing. Additionally, using subheadings, bullet points, and clear calls to action can improve readability and encourage users to interact with your content more effectively.